- How to create a file server cluster with Windows 2019
- Setting up a File Server Cluster
- Configure the file server cluster role
- Next steps and backup
- Scale-Out File Server for application data overview
- Scenario description
- In this scenario
- When to use Scale-Out File Server
- Practical applications
- Features included in this scenario
- Масштабируемый файловый сервер для обзора данных приложения Scale-Out File Server for application data overview
- Описание сценария Scenario description
- Содержание сценария In this scenario
- Когда использовать масштабируемый файловый сервер When to use Scale-Out File Server
- Практическое применение Practical applications
- Компоненты, используемые в данном сценарии Features included in this scenario
How to create a file server cluster with Windows 2019
High Availability of data and applications has been an important topic in IT for decades. One of the critical services in many companies is the file servers, which serve file shares where users or applications store their data. If the file server is offline, then people cannot work. Downtime means additional costs, which organizations try to avoid. Windows Server 2019 (and earlier versions) allow you to create highly available file services.
This blog describes how to create a file server cluster with Microsoft Windows Server 2019. An earlier blog post describes how to set up a Windows Failover Cluster (WFC) with Server 2019, while this blog post presumes that the failover cluster already exists.
Setting up a File Server Cluster
Before we can start with the file server cluster configuration, the file server role must be installed and permissions must be set in Active Directory for the failover cluster computer object.
There are two ways to install the file server role on the two cluster nodes:
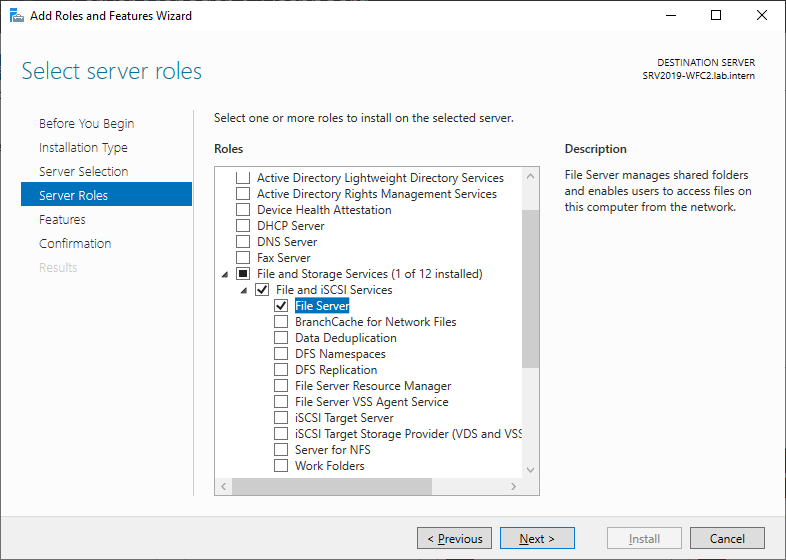
In Server manager, click Add roles and features and follow the wizard. Select the File Server role and install it. A reboot is not required.
As an alternative, you can use the following PowerShell command to install the file server feature:
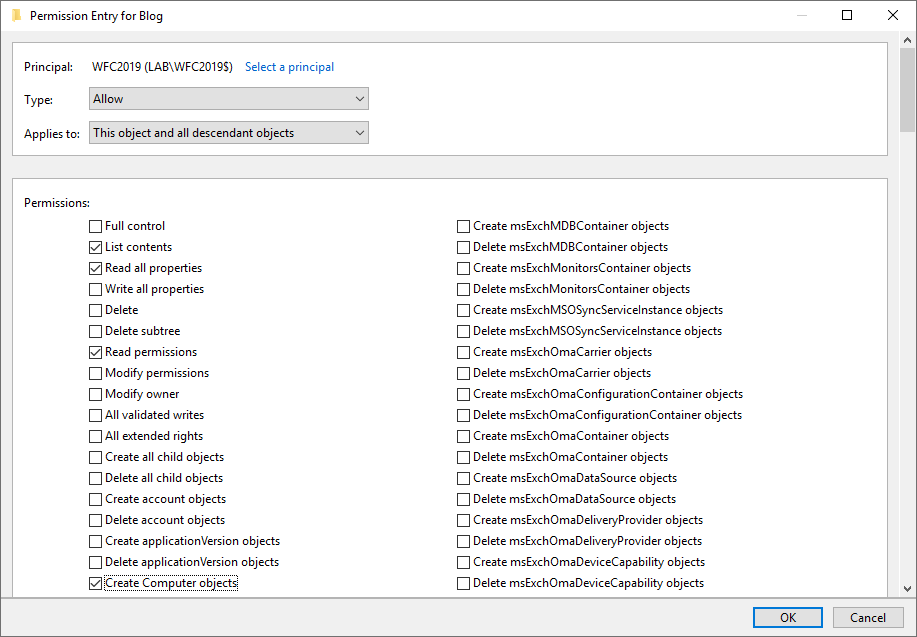
To avoid errors at later steps, first configure Active Directory permissions for the failover cluster computer object. The computer object of the cluster (in my case, WFC2019) must have the Create Computer Objects permissions in the Active Directory Organizational Unit (OU).
If you forget about this, the role will fail to start later. Errors and event IDs 1069, 1205 and 1254 will show up in the Windows event log and failover cluster manager.
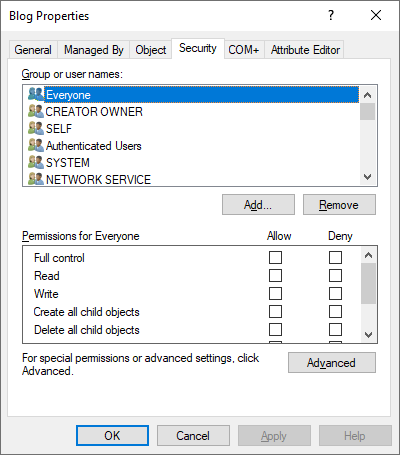
Open the Active Directory Users and Computers console and switch to Advanced Features in the View menu.
Go the OU where your cluster object is located (in my case the OU is Blog). Go to the Security tab (in properties) and click Advanced.
In the new window click Add and select your cluster computer object as principal (in my case WFC2019).
In the Permissions list select Create Computer objects
Click OK in all windows to confirm everything
Configure the file server cluster role
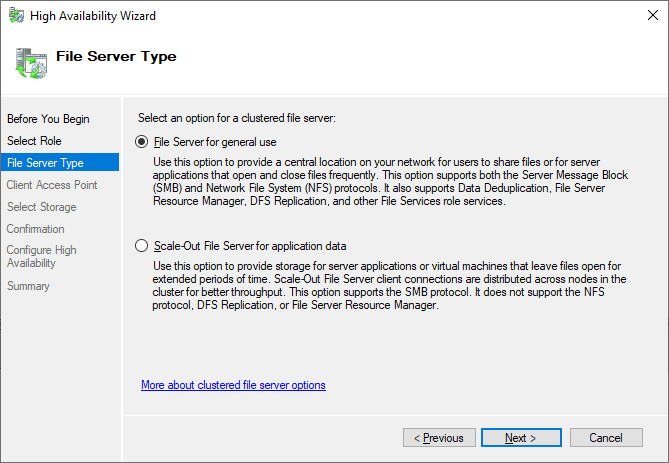
Because all pre-requisites are now met, we can configure the file server cluster role. Open the Failover Cluster manager and add the role to your cluster (right-click on Roles of your cluster -> configure role -> and select the File Server role).
We will create a file server for general use as we plan to host file shares for end users.
In the next step we define how clients can access the file server cluster. Select a name for your file server and assign an additional IP address.
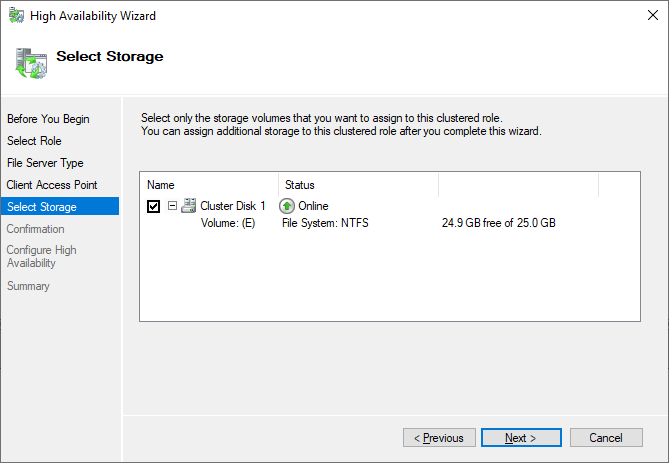
Use the storage configured earlier.
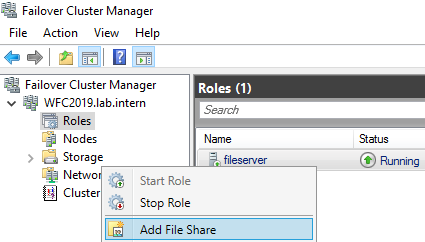
After you finish the wizard, you can see the File Server role up and running in the Failover Cluster Manager. If you see errors here, check the create computer objects permissions described earlier.
A new Active Directory object also appears in Active Directory Users and Computers, including a new DNS entry.
Now it’s time to create file shares for users. You can right-click on the file server role or use the actions panel on the right hand side.
I select the SMB Share – Quick as I plan a general purpose file server for end users.
I also keep the default permissions because this is just an example. After you have finished the wizard, the new file share is ready to use.
In the following video I show the advances of a continuous available file share. The upload of the file will continue even during a cluster failover. The client is a Windows 10 1809. I upload an iso to the file share I created earlier. My upload speed it about 10-20Mbit/s WAN connection. During failover to a different cluster node, the upload stops for some seconds. After successful failover it continues uploading the ISO file.
Next steps and backup
As soon as the file server contains data, it is also time to think about backing up the file server. Veeam Agent for Microsoft Windows can back up Windows failover clusters with shared disks. We also recommend doing backups of the entire system of the cluster. This also backs up the operating systems of the cluster members and helps to speed up restore of a failed cluster node because you don’t need to search for drivers, etc. in case of a restore.
Scale-Out File Server for application data overview
Applies to: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
Scale-Out File Server is designed to provide scale-out file shares that are continuously available for file-based server application storage. Scale-out file shares provides the ability to share the same folder from multiple nodes of the same cluster. This scenario focuses on how to plan for and deploy Scale-Out File Server.
You can deploy and configure a clustered file server by using either of the following methods:
Scenario description
With scale-out file shares, you can share the same folder from multiple nodes of a cluster. For instance, if you have a four-node file server cluster that is using Server Message Block (SMB) Scale-Out, a computer running Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2012 can access file shares from any of the four nodes. This is achieved by leveraging new Windows Server Failover Clustering features and the capabilities of the Windows file server protocol, SMB 3.0. File server administrators can provide scale-out file shares and continuously available file services to server applications and respond to increased demands quickly by simply bringing more servers online. All of this can be done in a production environment, and it is completely transparent to the server application.
Key benefits provided by Scale-Out File Server in include:
In this scenario
The following topics are available to help you deploy a Scale-Out File Server:
When to use Scale-Out File Server
You should not use Scale-Out File Server if your workload generates a high number of metadata operations, such as opening files, closing files, creating new files, or renaming existing files. A typical information worker would generate a lot of metadata operations. You should use a Scale-Out File Server if you are interested in the scalability and simplicity that it offers and if you only require technologies that are supported with Scale-Out File Server.
The following table lists the capabilities in SMB 3.0, the common Windows file systems, file server data management technologies, and common workloads. You can see whether the technology is supported with Scale-Out File Server, or if it requires a traditional clustered file server (also known as a file server for general use).
| Technology Area | Feature | General Use File Server Cluster | Scale-Out File Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMB | SMB Continuous Availability (*) | Yes | Yes |
| SMB | SMB Multichannel | Yes | Yes |
| SMB | SMB Direct | Yes | Yes |
| SMB | SMB Encryption | Yes | Yes |
| SMB | SMB Transparent failover | Yes (if continuous availability is enabled) | Yes |
| File System | NTFS | Yes | NA |
| File System | Resilient File System (ReFS) | Recommended with Storage Spaces Direct | Recommended with Storage Spaces Direct |
| File System | Cluster Shared Volume File System (CSV) | NA | Yes |
| File Management | BranchCache | Yes | No |
| File Management | Data Deduplication (Windows Server 2012) | Yes | No |
| File Management | Data Deduplication (Windows Server 2012 R2) | Yes | Yes (VDI only) |
| File Management | DFS Namespace (DFSN) root server root | Yes | No |
| File Management | DFS Namespace (DFSN) folder target server | Yes | Yes |
| File Management | DFS Replication (DFSR) | Yes | No |
| File Management | File Server Resource Manager (Screens and Quotas) | Yes | No |
| File Management | File Classification Infrastructure | Yes | No |
| File Management | Dynamic Access Control (claim-based access, CAP) | Yes | No |
| File Management | Folder Redirection | Yes | Not recommended |
| File Management | Offline Files (client side caching) | Yes | Not recommended |
| File Management | Roaming User Profiles | Yes | Not recommended |
| File Management | Home Directories | Yes | Not recommended |
| File Management | Work Folders | Yes | No |
| NFS | NFS Server | Yes | No |
| Applications | Hyper-V | Not recommended | Yes |
| Applications | Microsoft SQL Server | Not recommended | Yes |
Folder Redirection, Offline Files, Roaming User Profiles, or Home Directories generate a large number of writes that must be immediately written to disk (without buffering) when using continuously available file shares, reducing performance as compared to general purpose file shares. Continuously available file shares are also incompatible with File Server Resource Manager and PCs running Windows XP. Additionally, Offline Files might not transition to offline mode for 3-6 minutes after a user loses access to a share, which could frustrate users who aren’t yet using the Always Offline mode of Offline Files.
Practical applications
Scale-Out File Servers are ideal for server application storage. Some examples of server applications that can store their data on a scale-out file share are listed below:
If you use a scale-out file share as a library share, you can use only technologies that are compatible with Scale-Out File Server. For example, you can’t use DFS Replication to replicate a library share hosted on a scale-out file share. It’s also important that the scale-out file server have the latest software updates installed.
To use a scale-out file share as a library share, first add a library server (likely a virtual machine) with a local share or no shares at all. Then when you add a library share, choose a file share that’s hosted on a scale-out file server. This share should be VMM-managed and created exclusively for use by the library server. Also make sure to install the latest updates on the scale-out file server. For more information about adding VMM library servers and library shares, see Add profiles to the VMM library. For a list of currently available hotfixes for File and Storage Services, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 2899011.
Some users, such as information workers, have workloads that have a greater impact on performance. For example, operations like opening and closing files, creating new files, and renaming existing files, when performed by multiple users, have an impact on performance. If a file share is enabled with continuous availability, it provides data integrity, but it also affects the overall performance. Continuous availability requires that data writes through to the disk to ensure integrity in the event of a failure of a cluster node in a Scale-Out File Server. Therefore, a user that copies several large files to a file server can expect significantly slower performance on continuously available file share.
Features included in this scenario
The following table lists the features that are part of this scenario and describes how they support it.
Масштабируемый файловый сервер для обзора данных приложения Scale-Out File Server for application data overview
Применяется к: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012 Applies to: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
Scale-Out файловый сервер предназначен для предоставления масштабируемых файловых ресурсов, которые постоянно доступны для хранилища серверных приложений на основе файлов. Scale-Out File Server is designed to provide scale-out file shares that are continuously available for file-based server application storage. Масштабируемые файловые ресурсы обеспечивают возможность совместного использования папок различными узлами одного кластера. Scale-out file shares provides the ability to share the same folder from multiple nodes of the same cluster. Этот сценарий фокусируется на планировании и развертывании масштабируемого файлового сервера. This scenario focuses on how to plan for and deploy Scale-Out File Server.
Вы можете развернуть и настроить кластерный файловый сервер с помощью любого из следующих методов. You can deploy and configure a clustered file server by using either of the following methods:
Описание сценария Scenario description
Масштабируемые файловые ресурсы обеспечивают возможность совместного использования папок несколькими узлами одного кластера. With scale-out file shares, you can share the same folder from multiple nodes of a cluster. Например, при наличии кластера файлового сервера с четырьмя узлами, использующего горизонтальное масштабирование SMB, компьютер под управлением Windows Server 2012 R2 или Windows Server 2012 может получить доступ к общим папкам с любого из четырех узлов. For instance, if you have a four-node file server cluster that is using Server Message Block (SMB) Scale-Out, a computer running Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2012 can access file shares from any of the four nodes. Это достигается за счет использования новых компонентов отказоустойчивой кластеризации в Windows Server и возможностей протокола файловых серверов Windows — SMB 3.0. This is achieved by leveraging new Windows Server Failover Clustering features and the capabilities of the Windows file server protocol, SMB 3.0. Администраторы файловых серверов могут предоставлять масштабируемые файловые ресурсы и постоянно доступные файловые службы серверным приложениям, а также быстро реагировать на увеличение потребностей путем простого подключения к сети дополнительных серверов. File server administrators can provide scale-out file shares and continuously available file services to server applications and respond to increased demands quickly by simply bringing more servers online. Все это можно осуществлять в рабочей среде абсолютно прозрачно для серверного приложения. All of this can be done in a production environment, and it is completely transparent to the server application.
Основные преимущества масштабируемого файлового сервера включают следующее. Key benefits provided by Scale-Out File Server in include:
Содержание сценария In this scenario
Следующие разделы помогут вам развернуть масштабируемый файловый сервер. The following topics are available to help you deploy a Scale-Out File Server:
Когда использовать масштабируемый файловый сервер When to use Scale-Out File Server
Масштабируемый файловый сервер не следует использовать, если рабочая нагрузка создает большое количество операций с метаданными, например открытие и закрытие файлов, создание новых файлов или переименование существующих. You should not use Scale-Out File Server if your workload generates a high number of metadata operations, such as opening files, closing files, creating new files, or renaming existing files. Типичный пользователь, работающий с информацией, создает множество операций с метаданными. A typical information worker would generate a lot of metadata operations. Масштабируемый файловый сервер рекомендуется использовать, если важны масштабируемость и простота и требуются только те технологии, которые поддерживает масштабируемый файловый сервер. You should use a Scale-Out File Server if you are interested in the scalability and simplicity that it offers and if you only require technologies that are supported with Scale-Out File Server.
В следующей таблице перечислены возможности SMB 3.0, общие файловые системы Windows, технологии управления данными файловых серверов и общие рабочие нагрузки. The following table lists the capabilities in SMB 3.0, the common Windows file systems, file server data management technologies, and common workloads. Вы можете увидеть, поддерживается ли технология масштабируемым файловым сервером, или требуется традиционный кластерный файловый сервер (также известный как файловый сервер общего назначения). You can see whether the technology is supported with Scale-Out File Server, or if it requires a traditional clustered file server (also known as a file server for general use).
| Область технологий Technology Area | Функция Feature | Кластер файлового сервера общего назначения General Use File Server Cluster | Масштабируемый файловый сервер Scale-Out File Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMB SMB | Непрерывная доступность SMB (\*) SMB Continuous Availability (\*) | Да Yes | Да Yes |
| SMB SMB | Технология SMB Multichannel SMB Multichannel | Да Yes | Да Yes |
| SMB SMB | SMB Direct SMB Direct | Да Yes | Да Yes |
| SMB SMB | Шифрование SMB SMB Encryption | Да Yes | Да Yes |
| SMB SMB | Прозрачная отработка отказа SMB SMB Transparent failover | Да (если включена постоянная доступность) Yes (if continuous availability is enabled) | Да Yes |
| Файловая система File System | NTFS NTFS | Да Yes | Н/Д NA |
| Файловая система File System | Отказоустойчивая файловая система (ReFS) Resilient File System (ReFS) | Рекомендуется с Локальные дисковые пространства Recommended with Storage Spaces Direct | Рекомендуется с Локальные дисковые пространства Recommended with Storage Spaces Direct |
| Файловая система File System | Файловая система общего тома кластера (CSV) Cluster Shared Volume File System (CSV) | Н/Д NA | Да Yes |
| Управление файлами File Management | BranchCache BranchCache | Да Yes | Нет No |
| Управление файлами File Management | Дедупликация данных (Windows Server 2012) Data Deduplication (Windows Server 2012) | Да Yes | Нет No |
| Управление файлами File Management | Дедупликация данных (Windows Server 2012 R2) Data Deduplication (Windows Server 2012 R2) | Да Yes | Да (только VDI) Yes (VDI only) |
| Управление файлами File Management | Корень корневого сервера пространства имен DFS (DFSN) DFS Namespace (DFSN) root server root | Да Yes | Нет No |
| Управление файлами File Management | Целевой сервер папки пространства имен DFS (DFSN) DFS Namespace (DFSN) folder target server | Да Yes | Да Yes |
| Управление файлами File Management | Репликация DFS (DFSR) DFS Replication (DFSR) | Да Yes | Нет No |
| Управление файлами File Management | Диспетчер ресурсов файлового сервера (экраны и квоты) File Server Resource Manager (Screens and Quotas) | Да Yes | Нет No |
| Управление файлами File Management | Инфраструктура классификации файлов File Classification Infrastructure | Да Yes | Нет No |
| Управление файлами File Management | Динамический контроль доступа (доступ на основе утверждений, CAP) Dynamic Access Control (claim-based access, CAP) | Да Yes | Нет No |
| Управление файлами File Management | Перенаправление папок Folder Redirection | Да Yes | Не рекомендуется Not recommended |
| Управление файлами File Management | Автономные файлы (кэширование на стороне клиента) Offline Files (client side caching) | Да Yes | Не рекомендуется Not recommended |
| Управление файлами File Management | Проверка перемещаемых профилей пользователей Roaming User Profiles | Да Yes | Не рекомендуется Not recommended |
| Управление файлами File Management | Домашние каталоги Home Directories | Да Yes | Не рекомендуется Not recommended |
| Управление файлами File Management | рабочие папки Work Folders | Да Yes | Нет No |
| NFS NFS | Сервер NFS NFS Server | Да Yes | Нет No |
| Приложения Applications | Hyper-V Hyper-V | Не рекомендуется Not recommended | Да Yes |
| Приложения Applications | Microsoft SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server | Не рекомендуется Not recommended | Да Yes |
Перенаправление папок, автономные файлы, перемещаемые профили пользователей или домашние каталоги создают большое количество операций записи, которые должны немедленно записываться на диск (без буферизации) при использовании постоянно доступных файловых ресурсов, что снижает производительность по сравнению с общими файловыми ресурсами общего назначения. Folder Redirection, Offline Files, Roaming User Profiles, or Home Directories generate a large number of writes that must be immediately written to disk (without buffering) when using continuously available file shares, reducing performance as compared to general purpose file shares. Постоянно доступные файловые ресурсы также несовместимы с диспетчером ресурсов файлового сервера и ПК под управлением Windows XP. Continuously available file shares are also incompatible with File Server Resource Manager and PCs running Windows XP. Кроме того, автономные файлы может не переходить в режим «вне сети» на 3-6 минут после того, как пользователь теряет доступ к общей папке, что может привести к невозможности использовать режим «всегда автономный» автономные файлы. Additionally, Offline Files might not transition to offline mode for 3-6 minutes after a user loses access to a share, which could frustrate users who aren’t yet using the Always Offline mode of Offline Files.
Практическое применение Practical applications
Масштабируемые файловые серверы идеально подходят для хранилища серверных приложений. Scale-Out File Servers are ideal for server application storage. Ниже перечислены некоторые примеры серверных приложений, которые могут хранить свои данные в масштабируемом файловом ресурсе. Some examples of server applications that can store their data on a scale-out file share are listed below:
При использовании масштабируемого файлового ресурса в качестве общей папки библиотеки можно применять только те технологии, которые совместимы с масштабируемым файловым сервером. If you use a scale-out file share as a library share, you can use only technologies that are compatible with Scale-Out File Server. Например, репликация DFS нельзя использовать для репликации общей папки библиотеки, размещенной в масштабируемом файловом ресурсе. For example, you can’t use DFS Replication to replicate a library share hosted on a scale-out file share. Также важно наличие на масштабируемом файловом сервере установленных последних обновлений программного обеспечения. It’s also important that the scale-out file server have the latest software updates installed.
Чтобы использовать масштабируемый файловый ресурс в качестве общей папки библиотеки, сначала добавьте сервер библиотеки (скорее всего, это виртуальная машина) с локальной общей папкой или вообще без общих папок. To use a scale-out file share as a library share, first add a library server (likely a virtual machine) with a local share or no shares at all. Затем при добавлении общей папки библиотеки выберите общую папку, размещенную на масштабируемом файловом сервере. Then when you add a library share, choose a file share that’s hosted on a scale-out file server. Этот ресурс должен быть управляемым VMM и созданным исключительно для использования сервером библиотеки. This share should be VMM-managed and created exclusively for use by the library server. Также не забудьте установить последние обновления на масштабируемом файловом сервере. Also make sure to install the latest updates on the scale-out file server. Дополнительные сведения о добавлении серверов библиотек VMM и общих папок библиотек см. в статье Добавление профилей в БИБЛИОТЕКУ VMM. For more information about adding VMM library servers and library shares, see Add profiles to the VMM library. Список доступных в настоящее время исправлений для файловых служб и служб хранилища см. в статье базы знаний Майкрософт 2899011. For a list of currently available hotfixes for File and Storage Services, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 2899011.
Некоторые пользователи, например информационные работники, имеют рабочие нагрузки, которые значительно влияют на производительность. Some users, such as information workers, have workloads that have a greater impact on performance. Например, если такие операции, как открытие и закрытие файлов, создание новых файлов и переименование существующих файлов, выполняются несколькими пользователями, они оказывают влияние на производительность. For example, operations like opening and closing files, creating new files, and renaming existing files, when performed by multiple users, have an impact on performance. Если файловый ресурс включен с непрерывной доступностью, он обеспечивает целостность данных, но также влияет на общую производительность. If a file share is enabled with continuous availability, it provides data integrity, but it also affects the overall performance. Для постоянной доступности требуется сквозная запись данных на диск, чтобы обеспечить целостность в случае сбоя узла кластера на масштабируемом файловом сервере. Continuous availability requires that data writes through to the disk to ensure integrity in the event of a failure of a cluster node in a Scale-Out File Server. Таким образом, пользователь, который копирует несколько больших файлов на файловый сервер, может ожидать значительно более низкую производительность на постоянно доступном файловом ресурсе. Therefore, a user that copies several large files to a file server can expect significantly slower performance on continuously available file share.
Компоненты, используемые в данном сценарии Features included in this scenario
В следующей таблице перечислены компоненты, являющиеся частью данного сценария, и описано, как они поддерживают его. The following table lists the features that are part of this scenario and describes how they support it.